If you or a loved one are coping with liver health concerns alongside changes in your body, you may feel anxious or uncertain. It can be especially confusing when men notice unexpected breast tissue growth, without fully understanding why it happens.
At the Phoenix Gynecomastia Center, we frequently meet patients who face this combination of challenges. Gynecomastia is often linked to hormonal changes, but the important relationship between liver function and male breast enlargement is less widely recognized.
This connection is vital for achieving long-term health and the best gynecomastia surgery aesthetic results. Let’s explore how your liver affects gynecomastia, and what this means for your care and well-being.
Key Takeaways
- Liver and Hormones: The liver plays a crucial role in breaking down and regulating hormones that affect breast tissue growth.
- Common Liver Conditions: Diseases such as cirrhosis, hepatitis, and fatty liver disease are key contributors to gynecomastia in men.
- Recognizing Signs: Symptoms often go beyond breast tissue changes, including fatigue, jaundice, and swelling in the abdomen.
- Treatment Approaches: Addressing the underlying liver disease can sometimes reduce gynecomastia, but surgery is often necessary for lasting results.
- Assessment Process: Comprehensive evaluation at our practice includes liver function tests and hormone studies for safe surgery planning.
- Long-Term Outlook: Managing both liver health and gynecomastia improves confidence and supports overall well-being.
- Your Next Steps: If you suspect liver-related gynecomastia, our Phoenix team provides support, answers, and treatment options designed around your needs.

Understanding Gynecomastia: What Happens in the Body
Gynecomastia refers to the development of excess glandular breast tissue in males. The process is not simply an accumulation of fat, but rather the actual growth of breast gland tissue.
Hormonal imbalance remains the foundation of this process. An increase in estrogen or a decline in testosterone can trigger breast tissue growth. While this imbalance can sometimes be temporary, persistent cases require careful evaluation for underlying medical causes.
The relationship between hormonal changes and gynecomastia is especially significant when the liver is not functioning as it should. Subtle hormone shifts can occur without obvious symptoms, making early recognition essential.
Hormones Most Involved in Gynecomastia
Several hormones determine the balance between male and female features, even in men. The most critical for gynecomastia are:
- Estrogen: A small amount is naturally present in men and is responsible for some secondary sexual characteristics. Elevated levels encourage breast tissue growth.
- Testosterone: The dominant male hormone suppresses breast tissue growth. Low levels or reduced effectiveness create an imbalance.
- Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin (SHBG): The liver produces this protein, which regulates how much testosterone is available in the body.
Physical and Emotional Impact
Gynecomastia can cause more than just cosmetic concerns. Many men report tenderness or discomfort in the breast area. The change in appearance can lead to embarrassment, a drop in self-confidence, and social withdrawal. Recognizing this impact and the gynecomastia stage you’re in helps guide our supportive and comprehensive approach at the Phoenix Gynecomastia Center.
How the Liver Regulates Hormones
The liver is a master regulator of many body systems, including hormone metabolism. Its influence extends far beyond basic digestion and detoxification.
Every day, the liver processes and inactivates excess hormones in the blood. It is especially responsible for clearing estrogens and binding proteins that manage the balance of sex hormones. When liver function declines, this regulation falters, leading to subtle and sometimes dramatic hormonal shifts.
Liver’s Role in Hormonal Balance
The liver helps keep your hormones in check in several key ways:
- Metabolizing Estrogen: The liver breaks down estrogen into inactive forms, removing it from the body.
- Producing SHBG: This protein binds with testosterone and estrogen, controlling their activity levels.
- Supporting Testosterone: Indirectly, healthy liver function aids the body’s normal testosterone metabolism.
When these processes fail or slow, male estrogen levels may rise, testosterone levels fall, or both shift out of balance. This sets the stage for gynecomastia to develop or worsen.
Changes with Liver Disease
Once liver disease sets in, the body struggles to maintain its hormonal equilibrium. Estrogen is not cleared efficiently. SHBG levels may climb, further reducing the amount of free testosterone. This “dual hit” dramatically increases the risk of gynecomastia in men with chronic liver conditions.
Recognizing these patterns is essential for tailored and effective care.
Liver Diseases Most Often Linked to Gynecomastia
Several liver conditions dramatically increase the risk of gynecomastia. While not all men with liver problems develop breast tissue changes, certain diseases make the process more likely.
We will review the most significant liver diagnoses associated with gynecomastia, with explanations for how each affects your body.
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis refers to scarring of the liver, often due to chronic hepatitis, alcohol use, or other long-term damage. This scarring reduces the liver’s filter capacity and disrupts hormone metabolism.
Patients with cirrhosis often show visible signs of estrogen excess. These may include spider veins, red palms, and gynecomastia. Cirrhosis also disrupts SHBG levels, worsening hormonal imbalances.
Chronic Hepatitis
Ongoing hepatitis, whether caused by viruses or autoimmune disease, creates persistent inflammation in the liver. When chronic, hepatitis slowly impairs the liver’s hormonal management.
Men with hepatitis may not have obvious symptoms early on. However, hormonal disruption frequently precedes liver failure or cirrhosis, sometimes making gynecomastia one of the first warning signs.
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD results from the buildup of fat within liver cells, typically associated with obesity, diabetes, or metabolic syndrome. The excess fat creates inflammation and changes in liver function over time.
As NAFLD progresses, the liver’s ability to inactivate estrogen drops. Many men do not notice symptoms until the disease advances, making regular screening and awareness of physical changes important.
Liver Tumors
Certain benign and malignant liver tumors can disrupt hormone metabolism directly or by displacing healthy liver tissue. These cases are rare but underline why unexplained gynecomastia always deserves full evaluation.
Underlying liver tumors can produce hormones or interfere with normal hormone breakdown, emphasizing the need for thorough diagnosis.
Recognizing Symptoms: What to Watch For
Men with liver-related gynecomastia typically notice both breast tissue changes and other symptoms of liver dysfunction. Recognizing the complete symptom picture helps guide early intervention.
The following list highlights many signs you should be aware of if you suspect liver disease is connected to breast changes.
Common Symptoms of Liver Dysfunction and Gynecomastia
Patients typically experience a range of symptoms related to both liver dysfunction and breast tissue changes. It is important to be attentive to patterns and changes over time.
- Breast enlargement: Noticeable growth or swelling in one or both breasts is the hallmark sign of gynecomastia.
- Breast tenderness: Sensitivity or soreness may occur, even without visible swelling.
- Nipple changes: Some men see the nipple become puffier, and the skin may feel different.
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice): This signals a buildup of bilirubin, a common effect of liver dysfunction.
- Unexplained fatigue: Persistent tiredness often accompanies chronic liver impairment and affects daily quality of life.
- Abdominal swelling or discomfort: This may reflect fluid buildup or liver enlargement.
- Easy bruising or bleeding: The liver makes proteins that help blood clot, impaired function makes bruising more common.
Not every patient will experience all these symptoms. If you notice new breast development along with other concerning signs, scheduling a full evaluation is vital for accurate diagnosis.

How We Diagnose Liver-Related Gynecomastia
Diagnosis begins with your health story and a careful physical exam. At the Phoenix Gynecomastia Center, we believe a complete understanding is the foundation for safe treatment.
Testing typically includes several components, which together clarify both the liver problem and the cause of gynecomastia.
Medical History and Exam
We will discuss the timeline and details of your symptoms. Information about alcohol use, medication history, previous illnesses, and family health patterns guides our investigation.
A physical exam focuses on assessing the pattern of breast growth and looking for signs of liver disease or any additional causes of enlarged breasts in men.
Blood Work and Imaging Tests
We typically order tests such as:
- Liver function tests: These measure enzymes and proteins that indicate how well your liver works.
- Hormone panels: These include estradiol, total and free testosterone, LH, FSH, and SHBG.
- Ultrasound or other imaging: Visual scans of the liver may reveal scarring, tumors, or fat accumulation.
Our team uses these results to piece together the full puzzle and create a personalized treatment plan.
Treating Gynecomastia with Liver Disease
Treatment goals must reflect both cosmetic and medical priorities. By managing both liver health and gynecomastia, you gain better long-term results and support your overall well-being.
Addressing Liver Disease First
Achieving better control over the underlying liver condition can sometimes slow or reverse gynecomastia. This is especially true in early or mild disease.
- For hepatitis, antiviral or immune therapies may help.
- In alcohol-related disease, stopping alcohol and adopting a liver-healthy lifestyle are crucial.
- Metabolic disease management (weight loss, diet, managing diabetes) can slow fatty liver progression.
In advanced liver disease or when gynecomastia does not resolve, further treatment is considered.
Surgical Solutions
Once excess breast tissue develops, it rarely shrinks back to normal, especially if you have lived with liver disease for months or years. Surgery often provides the most effective and lasting relief.
We offer minimally invasive gynecomastia surgery at our Phoenix practice. The procedure removes glandular tissue and, if needed, excess fat and skin. This restores a more masculine chest contour.
The surgical approach is personalized. Patients with underlying liver disease may have increased bleeding risk or slower healing, so we plan procedures with exceptional care and monitoring.
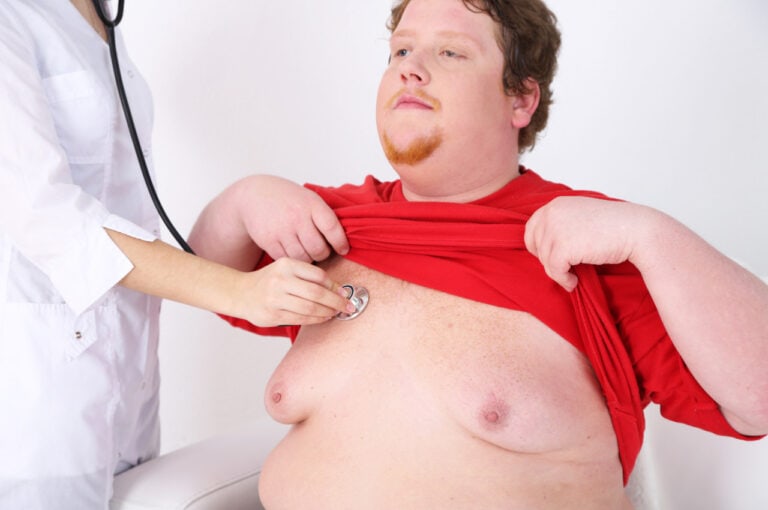
What to Expect Before, During, and After Surgery
Comprehensive care at the Phoenix Gynecomastia Center extends from before your procedure through your final results.
Preparing for Surgery
Preparation starts with making sure the liver condition is stable. You may need to pause certain medications that commonly cause gynecomastia, optimize your nutrition, or address bleeding risks. Preoperative lab work is essential.
Our surgeon will walk you through the plan, show you gynecomastia before and after results from previous patients, and answer every question so you feel confident moving forward.
The Day of Surgery
The procedure is typically performed on an outpatient basis, under general or local anesthesia with sedation. Gynecomastia surgery lasts one to two hours, depending on the amount of tissue removed and your unique anatomy.
You will return home the same day in most cases, with a support garment to minimize swelling.
Recovery and Results
Most men return to regular activity within a week, avoiding strenuous effort for several weeks. Healing may be slower if liver function is significantly compromised, so we tailor post-surgical guidance for every patient.
Visible improvements emerge quickly, but the chest contour continues to refine over several weeks. Your team will check progress closely and address any concerns promptly.
The majority of our patients feel a significant boost in physical comfort and self-confidence after surgery.
Preventing and Managing Recurrence
Liver-related gynecomastia carries a risk of recurrence, especially if liver disease progresses or new hormonal imbalances develop. Long-term prevention involves attention to both liver health and regular follow-up.
Long-Term Maintenance Care
Prevention begins with ongoing medical care for any liver diagnosis. This includes regular blood tests, medication management, and follow-up imaging when appropriate.
Healthy lifestyle choices are essential. Maintaining a normal weight, limiting alcohol intake, and choosing liver-friendly foods reduce the strain on your liver and help keep hormones in balance.
Communication remains vital. At our Phoenix center, we encourage you to contact us with any new breast changes, discomfort, or concerns about your liver. Early action is your best defense against recurrence and other complications.
Moving Forward with Confidence: Your Health and Body Image
Living with gynecomastia and liver disease presents unique challenges, but understanding the relationship between your liver health and breast tissue changes gives you an important tool in taking control of your well-being.
At the Phoenix Gynecomastia Center, we believe every patient deserves both medical safety and comfort with their appearance. Our team is always ready to guide you through diagnosis, answer your questions, and develop a truly personalized plan.
If you recognize any symptoms described above or have more questions about gynecomastia and liver health, we encourage you to reach out. Schedule a gynecomastia consultation with our Phoenix specialists, and take the next step toward a healthier, more confident future.

